Exploring the frontiers of semantic segmentation, adapting diffusion models for image to image, and tips for training diffusion models
Plus news headlines, research, and the problem with GenAI inference at the edge
What’s up, Community!
No major announcements from me, let’s get right to it!
🧐 What’s in this edition?
🗞️ The Sherry Code (News headlines)
🤩 Community Newsletter Exclusive
📰 The Deci Digest (Research and repositories)
🎨Tips and Tricks for Training a Diffusion Model
🖼️ Image-to-Image Translation with DeciDiffusion: A Developer’s Guide
🗞️ The Sherry Code: Your Weekly AI Bulletin
Shout out to Sherry for sharing her top picks for the AI news headlines you need to know about!
Sherry is an active member of the community. She’s at all the events, shares resources on Discord, and is an awesome human being.
Show some support and follow her on Instagram, Twitter, and Threads.
💸OpenAI tried to develop an AI model named after a dystopian hellscape in 'Dune,' but the project failed to land. Reports say that OpenAI's project Arrakis, aimed at cost-effective AI applications like ChatGPT, was scrapped in mid-2023 due to efficiency issues, marking a rare setback amid negotiations with Microsoft on a significant deal.
🤖 Adept has open-sourced Fuyu-8B, a simplified, fast multimodal AI model for digital agents. It supports arbitrary image resolutions and performs well on standard image understanding benchmarks, aiming to facilitate community-driven enhancements and applications.
😔 After ChatGPT disruption, StackOverflow lays off 28 percent of staff. StackOverflow, impacted by AI tools like ChatGPT, announced a 28% staff layoff. They're developing "Overflow AI" in response and are considering charging AI firms for data scraping.
⚙️ OpenAI updated its "Core values," emphasizing artificial general intelligence (AGI). Previously having six values, the new list prioritizes "AGI focus" and introduces values like "Scale" and "Team spirit.”
🧠 AI Could Help Brain Surgeons Diagnose Tumors in Real Time: A study introduced "Sturgeon," an AI model that rapidly diagnoses CNS tumours with 90% accuracy. This innovation aids surgeons in real-time tumour identification, enhancing treatment decisions.
Community Newsletter Exclusive: Exploring the Frontiers of Semantic Segmentation and Tackling Label Shifts
A while back, I had the opportunity to interview Dongwan Kim. He’s a Ph.D. student deeply involved in computer vision research. Our conversation went into some interesting aspects of deep learning and computer vision.
Here’s what we talked about:
Multi-Dataset Training: Dongwan presented a paper titled "Learning Semantic Segmentation from Multiple Datasets with Label Shifts." The challenge lies in training a single semantic segmentation model on various datasets.
Label Shifts & Conflicts: A significant issue he highlighted was "label shifts" or "label conflicts." The same object might have different labels depending on the dataset, posing a challenge for unified model training.
Evolving Granularity in Segmentation: We discussed the progression in segmentation datasets. Earlier datasets might label entities broadly, while newer ones delve into more granular classifications.
Solution to Label Conflicts: Dongwan introduced an innovative solution using "multi-hot labels," a departure from the traditional "one-hot labels." This approach addresses the label conflict problem uniquely.
Data-Centric Approach: Our discussion discussed the ongoing debate between data-centric and model-centric AI. Dongwan's work leans more towards the data-centric approach, emphasizing the value of expansive training on multiple segmentation datasets.
For those keen on the technical nuances and advancements in semantic segmentation, Dongwan's insights and research provide a fresh perspective on tackling prevalent challenges in the field.
📰 The Deci Digest
🏘️ Meta AI's Fundamental AI Research (FAIR) introduced a trio of resources aimed at simplifying, expediting, and reducing the costs associated with robotics research. These consist of Habitat 3.0, the Habitat Synthetic Scenes Dataset, and HomeRobot.
🕵️ A research team from the Allen Institute of AI, the University of Arizona, and the University of Penn presented CLIN (Continually Learning Language Agent), an innovative architecture that empowers language agents to enhance their performance.
🤖 Researchers from UT Austin developed LIBERO, a specialized benchmark designed to align with the principles of lifelong robot learning with the capacity for continuous growth.
🌳 The Univerisity of Science and Technology of China and TencentGlobal YouTu Lab researchers created a groundbreaking framework, "Woodpecker," designed to correct hallucinations in multimodal large language models.
🛍️ Amazon is currently in the beta testing phase for a GenAI tool that creates images for advertisers by using product descriptions and themes as references.
Tips and Tricks for Training a Diffusion Model
In this video, I provide a comprehensive walkthrough of the innovative techniques and strategies that power DeciDiffusion.
What You'll Learn:
In-depth Understanding of DeciDiffusion: Discover the architectural brilliance and training methodologies that set DeciDiffusion apart.
Expert Insights: Gain valuable insights into the cutting-edge architecture and training strategies that drive DeciDiffusion's success.
Best Practices for Accelerating LLM Inferences: Equip yourself with actionable strategies to supercharge LLM inferences, giving your applications a distinct advantage.
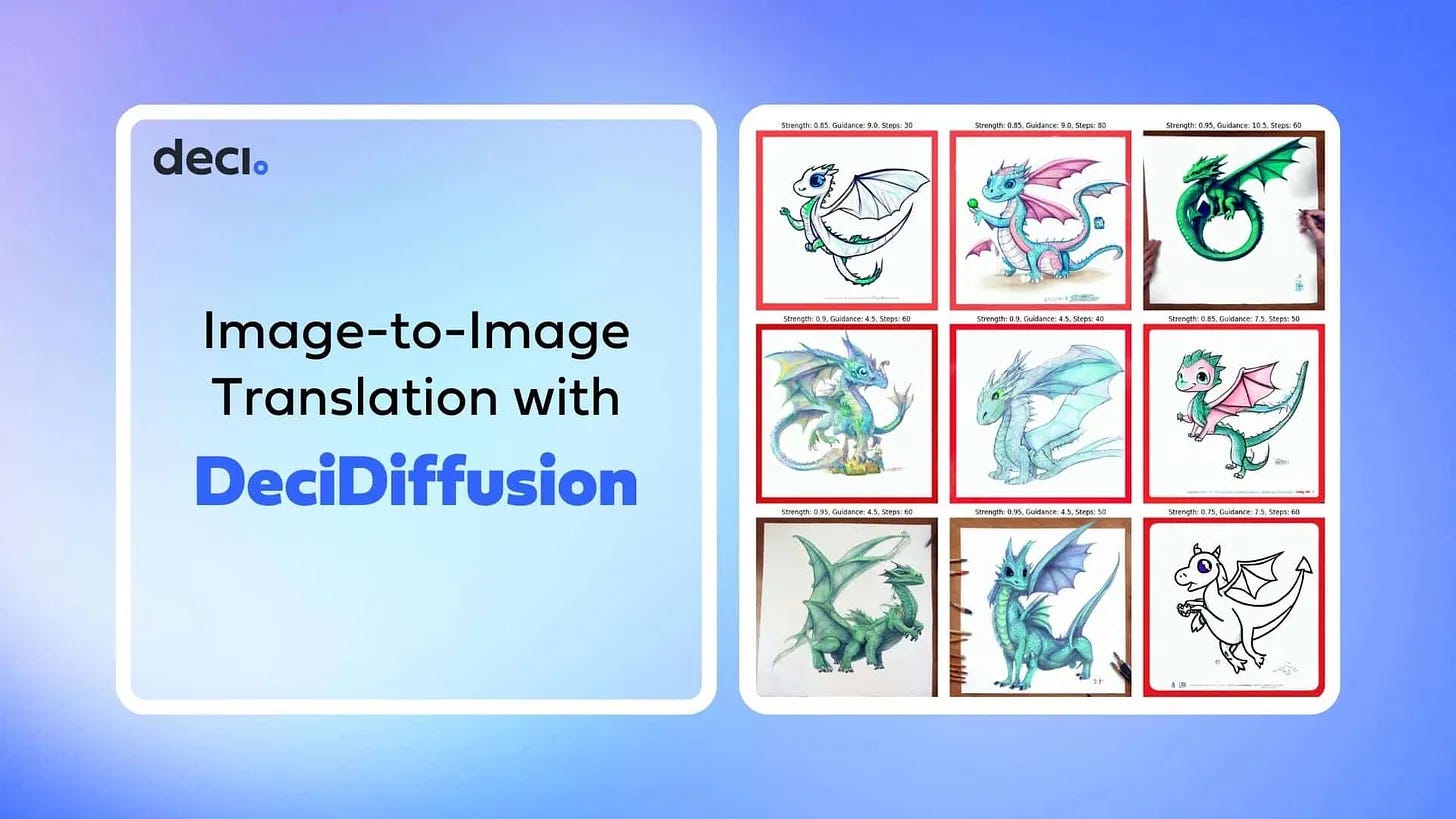
Image-to-Image Translation with DeciDiffusion: A Developer’s Guide
Learn how to adapt DeciDiffusion for diverse image-to-image translations using our detailed guide. From turning sketches into vibrant artwork to day-to-night transitions, harness the might of this 1.02 billion-parameter model to drive innovation in various visual applications.
What You'll Learn:
Introduction to DeciDiffusion: Discover the capabilities of DeciDiffusion, a robust text-to-image latent diffusion model developed by Deci, and how it surpasses other models in delivering high-quality images.
The Science Behind Image-to-Image Translation: Understand the intricacies of translating one image to another while retaining its essence and the challenges faced in this domain.
Diving into SDEdit: Learn about HuggingFace’s Diffusers Library Technique, which uses Stochastic Differential Editing for image-to-image diffusion.
Instantiating and Adapting DeciDiffusion: A step-by-step guide on how to adapt DeciDiffusion for image-to-image tasks, including using specialized UNet-NAS.
Understanding Generation Parameters: Dive deep into the parameters like strength, guidance scale, and steps that play a pivotal role in determining the quality of the generated image.
Conclusion: Reflect on the power of img2img diffusion in image processing and the advancements brought by DeciDiffusion.
Harnessing Generative AI: The Inference Impasse and the Path Ahead
Generative AI has the potential to hold intelligent dialogues, craft complex codes, and generate enthralling imagery. Yet, as it steps into the real-world application, the allure meets the arduous reality of inference, particularly at the edge where resources are scant.
One primary adversary is the resource constraints on edge devices.
Generative models often find themselves ill-equipped in memory and computational prowess to host the traditionally large machine learning models, let alone efficiently run inference tasks. The conventional models falter in capturing long-range dependencies in sequential data, a crucial ability to understand complex relationships inherent in language or time series data1.
The narrative of cost, power, and scalability further thickens the plot.
Generative AI, while remarkable, demands a heavy toll on computational resources, driving up infrastructure costs significantly. The reliance on cloud-based servers with power-hungry GPUs is a hefty affair, with AI-enabled servers costing up to seven times more than regular servers. The energy consumption of these servers is another beast to tame, with data centers housing them guzzling an alarming amount of power, projecting a grim forecast of worldwide power consumption if the current trends persist2.
Scaling the generative AI services, a vision many companies harbour unveils another layer of complexity. The sheer size of generative models, boasting billions of parameters, necessitates a colossal amount of computational power for inference. The dilemma of scaling while keeping the costs in check is a pressing concern for companies aspiring to leverage generative AI for better efficiencies and improved workflows3.
Yet, amidst these challenges, the glimmers of solutions are visible on the horizon.
The inception of transformer architectures heralds a new hope, offering a pathway to increase computational efficiency significantly. Their parallel nature makes them a worthy companion for resource-constrained edge devices. Model compression further augments this hope, where techniques like knowledge distillation and pruning enable the creation of compact transformer models without compromising accuracy1.
The shift of generative AI compute workloads to the edge is another promising stride. It addresses the quintessential concerns of cost, power, and scalability while enhancing privacy and reducing latency, a significant move to make generative AI more accessible and efficient2.
The path of Generative AI, though laden with challenges, is not devoid of solutions.
As the narrative of generative AI continues to unfold, the collaborative efforts from the industry, academia, and policymakers will be paramount in addressing the inference impasse and propelling Generative AI into a future where it can realize its full potential.
References:
Semi Engineering: "Generative AI: Transforming Inference At The Edge" - Discusses the challenges of running inference on resource-constrained edge devices and how transformer models can help overcome these challenges1.
Unite.AI: "The Future of Generative AI Is the Edge" - Addresses the cost, power, and scalability issues when running Generative AI models in the cloud, advocating for moving compute workloads to the edge to mitigate these challenges2.
The Register: "Automating generative AI development" - Highlights the scaling challenges companies face when developing generative AI services and the substantial computational power required for inference due to the large size of generative models3.
That’s it for this week!
Let me know how I’m doing.
Cheers,